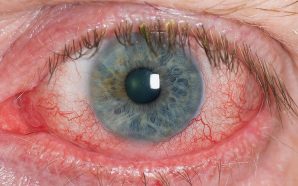
Nowadays, several adults possess a particular kind of gum disease. Gum diseases are commonly called a periodontal disease which affects the tissues and bones surrounding the teeth. Gum diseases vary into a disorder that is serious between gum inflammations that are plain, resulting into tissues that sustain the teeth and the bone into damages.
You will find 2 separate phases of gum diseases. While periodontitis is the next stage, the first stage is referred to as gingivitis. It is quite probable to possess a gum disease in the event you smoke or do not wash your teeth well.
What causes Gum Disease?
Plaque is the major cause of gum diseases. Other factors may lead to the periodontal disease. The factors include:
- Hormonal changes like those that occur during puberty, menopause, pregnancy and yearly menstruation. This makes the gum to be more sensitive thus making it much easier for the growth of gingivitis.
- Illnesses might also alter the condition of the gums. These include diseases like cancer and HIV that hinder your immune system.
- Medicines may also affect dental health since some generally reduce saliva flow saliva; a fluid that has protective effects in your teeth and gums. Some drugs such as anticonvulsant drugs Dilantin and anti-angina drug lead to an abnormal development of the gum disease.
- Bad habits such as smoking create it quite difficult for the chewing gum tissues to repair it self.
- Poor oral hygienic habits just like never flossing and brushing your teeth on daily basis.
Genealogy and family history of dental diseases is also one of the contributing factors behind the diseases.
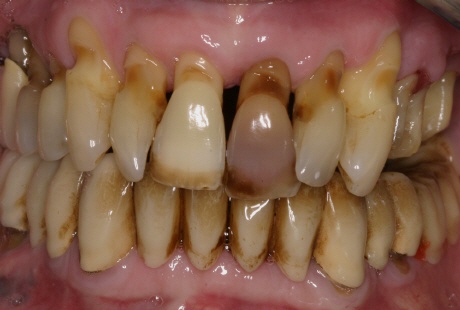
Gum disease could grow painlessly only by producing several obvious signs and symptoms even in late stages of this disease. The problem is not totally without warning having signs, even though indicators of diseases in many cases are quite subtle. Symptoms could point out a types of this disease. The symptoms of the illness include:
- Gums that bleed throughout and after tooth brushing
- Red, swollen and tender teeth
- Continuous bad breath and bad taste in your mouth
- Receding gums
- the forming of pockets between gums and teeth
- Loose and even changing teeth
- Changes at the ways the teeth fit together after scratching.
Even in the event that you do not observe any signs and symptoms, you may still have any rates of gum diseases. In some individuals, certain teeth could affect just like the molars. Periodontists determine the development of the disease and or a dentist may recognize.
Risk Factors For Gingivitis
- Chewing or smoking tobacco
- diabetes
- swallowing some medications (steroids, anticonvulsants, oral meds, chemotherapy and calcium channel blockers)
- crooked teeth
- cracked fillings
- dental appliances that fit poorly
- pregnancy
- hereditary variables
- compromised resistance (such as HIV/AIDS patients)
How Is Gum Disease Treated?
The principal aims of chewing gum disease treatments are boosting reattachment of the nutritious gums to your teeth ; reduce swelling, and reduce the thickness of pockets, and reduce the chance of ailments and stop disease development.
Treatment options usually are contingent on the stages of the disease, how you might have responded to the earlier treatments plus one’s overall wellbeing. Treatment ranges from non surgical therapies which control the increase of bacterial to surgeries so as to bring back the tissues that are supportive.