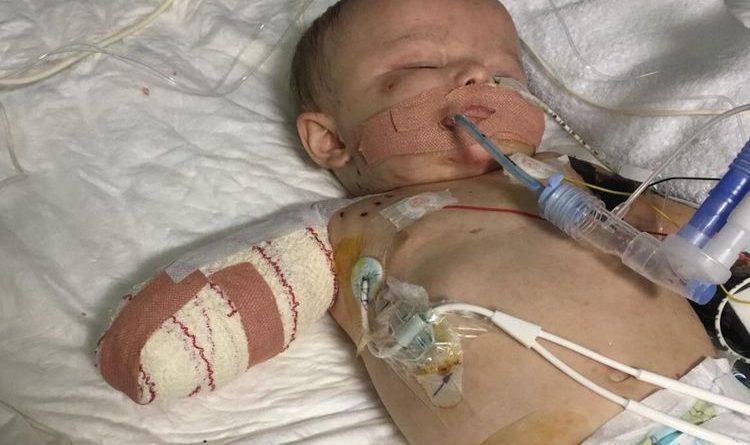
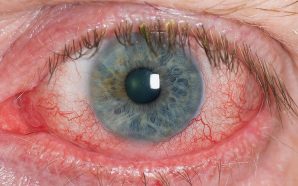
Meningitis happens if the membranes surrounding your brain and spinal cord become inflamed. The swelling that results is usually what causes the most famous symptoms of this illness: fever, headache, and stiff neck. Depending upon the reason for the illness that triggers meningitis, it may progress on its own or require emergency antibiotic treatment.
Knowing which kind of illness has triggered a case of meningitis may be the initial step in selecting the right treatment. Besides the reasons mentioned below, meningitis can also lead from non infectious causes of occasion, such as chemical reactions, drug allergies, some types of cancer, diabetes, and inflammatory diseases like sarcoidosis.
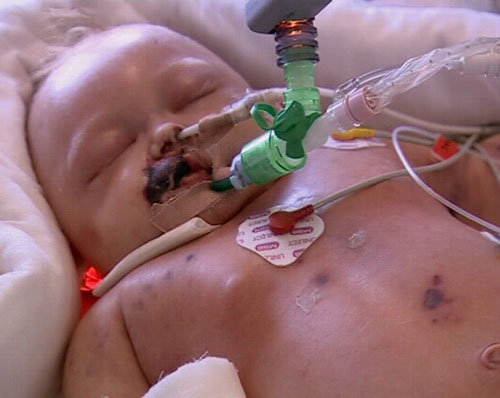
Viral Meningitis
Viral infections are the most frequent cause of meningitis cases within the USA. Viral meningitis is generally accompanied with milder symptoms and is effective at clearing up by itself. In the U.S., a group of viruses called enteroviruses is responsible for most cases of viral meningitis. These viruses are most common in the late summer and early autumn. There are several other viruses that can lead to viral meningitis, such as herpes simplex virus, HIV, mumps, and West Nile.
Bacterial meningitis typically occurs when bacteria enter the blood and migrate to the brain and spinal cord. However, it can also happen when bacteria directly invade the meninges because of an ear or sinus infection, a skull fracture, or after a operation. There are a few unique breeds of bacteria that can cause bacterial meningitis. The most typical are:
- Streptococcus Pneumoniae (pneumococcus) — This sort of illness is most common in infants, small children, and adults. There is currently a vaccine to help reduce the occurrence of this illness. It is an extremely contagious strain, however there’s a vaccine to decrease the probability of this illness.
- Haemophilus Influenzae (haemophilus) — This breed was the chief cause of bacterial meningitis in children in the USA, however now new vaccines have significantly diminished the number of cases. It most often affects people who have weakened immune system, such as elderly women, teens, and older adults. Listeria gets the power to cross the placental barrier, therefore it can cause infections which will result in a baby being stillborn or dying right after arrival.Fungal meningitis is relatively rare and will result in chronic meningitis. This sort of meningitis is not contagious. It most often affects people who have immune deficiencies like AIDS, plus it is lifethreatening or even treated with antifungal medications as soon as possible. The most frequent fungal form of the disease is cryptococcal meningitis.
Chronic Meningitis
Chronic meningitis happens when slow-growing organisms, like parasites, invade the membranes and fluids surrounding your brain. Unlike other forms of meningitis, chronic meningitis develops over a few weeks, even although the signs and symptoms are the exact same as examples of acute meningitis — nausea, nausea, nausea, and mental cloudiness.