Whilst clotting is a normal and balanced response of the blood to a cut or wound, sometimes a blood clot hurts more than it helps. Blood clot, or even a thrombus, can cause a host of issues with its own presence within the system. The flow of blood is restricted in the areas beyond the uterus, that causes issues such as a lack of oxygen (ischemia) from the cells beyond the blood or clot pooling because of poor circulation–that contributes to swelling, tenderness, and other ailments.
Of course, the exact damage and issues that result from a thrombus depend largely upon where from your body the clot strains. In addition, one of the very threatening aspects of a thrombus is that it will not always stay stuck. Here is just a look at what goes on in sections of your body when a blood clot forms.
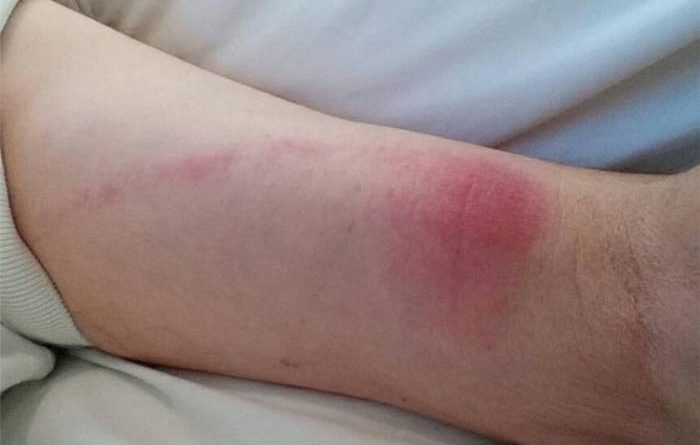
But not as commonly clotting issues can occur in the arm. This really is known as phlebitis if a thrombus forms from the legs near the skin. Shallow phlebitis can be dealt with fairly readily, although there might be swelling, discoloration, or some discomfort.
It can, however, cause the blood vessels to harden, a disease to grow up, or –perhaps most seriously–be indicative of the maturation of deep vein thrombosis. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT), thus named as it forms from the veins deep from the leg or other slips, can also cause swelling and pain however may be asymptomatic some times. And if you do not understand it’s there, you do not understand You Have to get it treated.
Postphlebitic syndrome might be a potential complication of DVT, in which blood flow isn’t as efficient in the area as a result of harm to the bloodstream caused by the blood clot. Again, of clotting from the extremities, the danger is the prospect of the thrombus to become an embolus.
The lungs are an extremely dangerous area to develop a clot. A pulmonary embolism is a significant complication which might happen from developing a clot elsewhere in your system (especially from DVT). The thrombus travels around the torso, breaks loose, and lodges from the vessels that cause the lungs. This can lead to shortness of breath, chest pain, increased heartbeat, dizziness, and coughing up blood. It may be fatal if left untreated.
Clotting from the Brain
An cerebral embolism describes a clot which forms in one’s center or carotid arteries which break loose and travels to the brain, resulting in an ischemic stroke. Brain cells start to die after only a couple of minutes without blood, resulting in vision issues, difficulty discussing, headaches, a lack of coordination, and sometimes even muscle weakness or paralysis (typically using 1 side of their human anatomy).
Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis is an uncommon sort of stroke brought on by a blood clot forming at the venous sinuses. Blood is unable to leave mental performance, and also the cells start to break, finally resulting in a hemorrhage. The indicators of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis are very similar to that of a ischemic stroke, even although even a coma are other likely issues that can result.