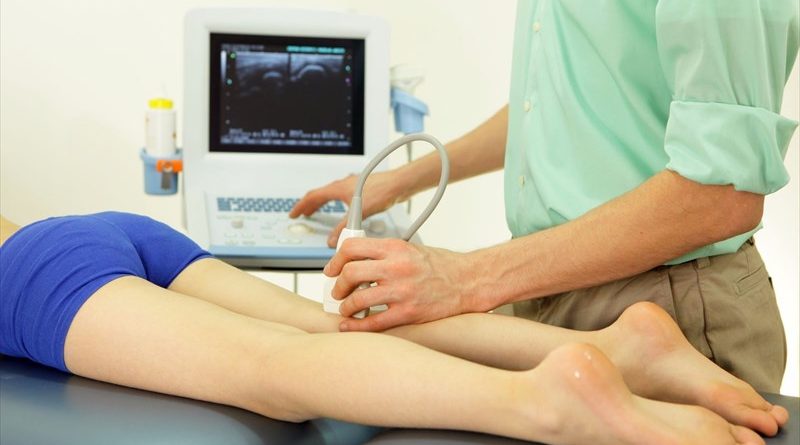
You will notice pain or swelling in the calves, or there could be no symptoms at all. Although these may appear light, DVT is a serious medical condition that experts recommend prompt care. The more you know about requirements such as DVT, the more capable you are to safeguard yourself out of them or to manage them properly if they appear.
- Thrombus: Thrombus (as in “thrombosis”) is the clinical term for a blood clot. Whenever you receive wounded, the clotting functionality compels to prevent excessive bleeding. Sometimes, that clotting activates in blood vessels, and also the platelets and different things which constitute blood become a mass which may impede blood flow.
The clot which forms isn’t held indefinitely set up. It might shake loose, travel through the blood vessels and block a blood vessel in the lungs. Indications of a pulmonary embolism include chest pain, difficulty breathing, dizziness, a rapid heartbeat, and coughing up blood.
Literally, it’s the blood clot (a deep vein thrombus specifically) breaking loose, travel around, and winding up in the lungs.
- Postphlebitic syndrome: Construction DVT may cause postphlebitic syndrome, even if the blood vessels around the clot have been all damaged. Blood can no longer flow too easily, resulting in swelling or pain of their thighs and discoloration or sores on the skin. It can take years for symptoms to be observable.

Clotting occurs repeatedly, that causes the location affected to eventually become very painful, bloated, and turn blue or white. The odds of developing a pulmonary embolism are increased, and also the bloodflow could be cut off into the scope which gangrene can place in.
- D-Dimer: D-Dimer is really a compound that your body releases when blood clots dissolve. Therefore, it is also a blood test used to look for clots in the veins. A positive result does not necessarily signify DVT, as other things may cause D-Dimer manufacturing, such as pregnancy or falling. This means the d-dimer test needs to be applied carefully and with additional evaluations are often used in conjunction.
- Anticoagulant: People with clotting disorders and other others at a higher risk for having a clot usually are placed on an anti coagulant, or blood thinner. It can help discourage cells from multiplying as easily.
- Virchow’s Triad: The three aspects of Virchow’s Triad explain how D VT forms. Venous stasis, hypercoagulability, and injury to the bronchial lining of their veins all play a role in the clot of the formation, and enables the clinical community know contributing factors into DVT.
- Venous stasis: This first part of Virchow’s triad describes an alteration in blood flow–specifically, it slows down. A sedentary lifestyle or sitting for a long time, such as during a car trip or throughout the recovery period of a disorder, give rise to the development of DVT. It’s particularly important to go the legs as much as you can during these instances.
- Hypercoagulability: Hypercoagulability means an increased risk for having a clot. It could be because of blood disease, cancer, age, or pregnancy, along with other things which make the blood clot more easily. Just because a person is in a hypercoagulative state doesn’t mean they’ll absolutely develop a clot, however it is vital to be careful.